39 week of pregnancy fetal position. Unpleasant signs and symptoms during this period. Changes in the female body
 The body weight of the fetus at the 39th week can fluctuate within 3403 plus or minus 415 g, most often averaging 3300 g. The baby’s body length at the 39th week fluctuates within 50.8 plus or minus 1.6 cm, the most often averaging 51 – 52 cm. In general, the size of the fetus at the 39th week can vary significantly among different women, as they depend on the individual constitution and nature of the mother’s diet. For example, a child of large, broad-boned parents will naturally have greater height and weight compared to a baby whose father and mother are short, thin and thin-boned.
The body weight of the fetus at the 39th week can fluctuate within 3403 plus or minus 415 g, most often averaging 3300 g. The baby’s body length at the 39th week fluctuates within 50.8 plus or minus 1.6 cm, the most often averaging 51 – 52 cm. In general, the size of the fetus at the 39th week can vary significantly among different women, as they depend on the individual constitution and nature of the mother’s diet. For example, a child of large, broad-boned parents will naturally have greater height and weight compared to a baby whose father and mother are short, thin and thin-boned. In general, by the 39th week, the development of the fetus has already been completed, all organs are formed and working in training mode, they are completely ready for normal functioning outside the womb. And in the last weeks of being in the uterus, the fetus intensively trains the work of the internal organs, achieving their coordinated and well-functioning activity.
The baby does not move constantly and with unequal frequency and intensity throughout the day, since he has a sleep and wakefulness pattern. That is, the fetus alternately sleeps and is awake. Accordingly, when he sleeps, he is motionless, and when he is awake, he moves. It is almost impossible to predict when the baby will sleep and when to move - he has his own sleep and wakefulness schedule. However, there are a number of interesting patterns, taking into account which we can roughly predict when the baby will move and when he will sleep.
So, when the mother actively moves, for example, walking down the street, working around the house, or periodically getting up and sitting down, her stomach sways, which creates the effect of motion sickness for the child. Therefore, the baby usually sleeps and does not move during the mother’s movements. He is simply rocked by the light and steady swaying of his belly. But as soon as the mother sits down or lies down to rest, the baby begins to move. This is explained by the fact that in a sitting or lying position the mother’s belly does not sway, there is no motion sickness effect, the fetus wakes up and begins to move. Accordingly, a woman should expect more active and frequent movements of the baby when she is in a state of complete rest: resting, sleeping, etc. But when the mother herself is actively moving, we can expect that the fetus will lie quietly and not move.
In addition, after the mother eats, the baby also usually begins to move actively. This is due to the fact that the concentration of glucose in the blood increases, which it uses to produce energy, and then spends this energy for its movements and movements.
In addition to the baby's movements, a woman may periodically feel rhythmic tremors inside her abdomen. It's okay, the baby is just hiccupping. Such hiccups are not dangerous for the baby and usually go away quickly.
A woman should feel fetal movements every day, but she should not count their number hourly, as this will only bring unnecessary anxiety and will in no way help control the baby’s condition. After all, as mentioned above, the baby alternately sleeps and is awake, and at the hour when he sleeps, the frequency of movements will be low or the fetus will not move at all. Therefore, there is no need to count movements every hour; it is enough to count their number over 12 hours. If in 12 hours the fetus moves 10 - 12 times, then everything is in order. If the baby moves less than 10 times in 12 hours, then it is necessary to call an ambulance and be hospitalized in the maternity hospital so that doctors can provide assistance and save the child from death.
Ultrasound and tests
At the 39th week, women who underwent examinations and were observed in consultation during pregnancy are not routinely prescribed an ultrasound scan, as this is not necessary. An ultrasound at this stage can be prescribed only for a specific purpose: to confirm or identify pregnancy complications that were suspected only at the 39th week. In addition, an ultrasound may be prescribed for women who need to be hospitalized in a maternity hospital in advance, before the expected date of birth.If a woman has not been examined even once during her entire pregnancy, she may be prescribed a routine ultrasound to assess the condition of the uterus, cervix, placenta, umbilical cord and fetus, to identify the position and presentation of the fetus, as well as to determine whether the baby’s development is normal. .
Much more often, at the 39th week, cardiotocography can be prescribed, which makes it possible to detect fetal hypoxia and disorders caused by circulatory disorders in the mother-placenta-fetus system. If fetal hypoxia is suspected, CTG is prescribed in order to promptly confirm this and carry out early delivery so that the baby does not suffer for some time in the womb from oxygen deficiency.
 Cardiotocography at 39 weeks may be prescribed if a woman has the following conditions or diseases:
Cardiotocography at 39 weeks may be prescribed if a woman has the following conditions or diseases:
- Suspicion of the umbilical cord entwining the fetal neck;
- Abnormal heartbeat (fast or rare) in the baby;
- Oblique or transverse position of the fetus in the uterus;
- Suspicion of cardiac or central nervous system malformations in the fetus;
- Suspicion or previously identified pathology of the placenta (early aging, small thickness, placenta previa);
- One umbilical artery;
- Oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios;
- Preeclampsia;
- Fetal growth retardation according to fetometry;
- Diabetes mellitus or hypertension in a pregnant woman;
- Rh conflict in women with negative Rh factor blood, identified based on determination of antibody titer.
The risk of preeclampsia is considered high if there is protein in the urine. In such situations, preventive treatment is prescribed aimed at preventing this complication, which consists of taking calcium (1 g per day until the 40th week inclusive). The risk of preeclampsia is considered low if there is no protein in the urine, in which case preventive therapy is not given.
If, in addition to protein in the urine, a woman has severe edema, high blood pressure and visual disturbances such as the flickering of spots and spots before the eyes, then this indicates the presence of gestosis. And gestosis is also a formidable complication of pregnancy, the course of which is unpredictable: at any moment the woman’s condition can deteriorate so much that both she and the fetus die. Therefore, when gestosis is detected, the doctor immediately sends the woman to the maternity hospital, where obstetricians provide medication preparation so that the mother’s body can endure childbirth, after which an early delivery is performed by cesarean section or induction of natural labor. It is useless to treat gestosis at the 39th week, since this complication cannot be cured, and it can only be eliminated by terminating the pregnancy. And since at the 39th week the fetus is already mature, it is possible to terminate the pregnancy, thereby eliminating the complication for the mother and minimizing the risk of fetal death.
When leukocytes, red blood cells, casts, mucus, bacteria or epithelial cells are detected in the urinary sediment, this is a sign of diseases of the urinary system. In this case, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment before birth, so as not to infect the baby and to undergo the birth process normally.
There is no need to take any other tests at week 39 unless your doctor prescribes them.
Visiting an obstetrician-gynecologist
At the 39th week, you should routinely visit an obstetrician-gynecologist for consultation, if you do not need to go to the maternity hospital for prenatal hospitalization. In this case, the date of the visit must be calculated in such a way that 7–8 days have passed since the last visit. If this date falls on a weekend, then it is better to go to the gynecologist on Monday of the next, 40th week, since the interval between visits from the 37th to the 40th week can vary from 7 to 10 days.You need to take with you to the doctor documents and all the results of tests and examinations that the doctor has not yet seen - based on them, he will draw a conclusion about whether you need to go to the maternity hospital for delivery or whether you can carry the pregnancy to term at home, waiting for the natural onset of labor.
At the beginning of the appointment, the doctor asks a number of questions that help identify signs of pregnancy complications, as well as assess the condition of the woman, the fetus and their readiness for childbirth. During a conversation, an obstetrician-gynecologist usually asks questions along the following lines:
- What symptoms bother a woman, how often do they appear, what provokes them, how can they be stopped?
- How often does a woman feel fetal movements, how many movements are felt within 12 hours, when was the last time she felt the baby move?
- Do you experience bloody vaginal discharge?
- Has the nature of the discharge changed, was there anything unusual about it, was there any discharge that caused discomfort, pain, itching or burning?
- What is the nature of the discharge from the genital tract (color, smell, quantity, consistency, impurities, etc.)?
- Does the vagina occasionally discharge a relatively large amount of cloudy, yellowish water with a sweet taste and smell (the sweetness causes the skin in the perineum and inner thighs to feel sticky)?
- Is there a feeling of wetness in the perineum or periodic unexplained wetting of underwear?
- Do you have frequent or persistent headaches?
- Are there visual impairments such as the flickering of flies, spots, flashes, transparent spirals before the eyes?
- Is there redness, swelling, burning or itching in the genital area?
- Do you have pain and/or burning when urinating and lower back pain?
- What is the nature of abdominal pain, how have they changed over the last week, when do they occur, how long do they last, what causes them to go away?
- Do you experience sudden severe swelling of the hands and face?
A breast examination is performed to assess its condition and readiness for breastfeeding, as well as to identify lumps and mastitis. The legs are examined to identify varicose veins and assess the degree of swelling. The skin is examined to identify any rashes, redness or inflammation. The anterior abdominal wall is examined to assess the degree of muscle elasticity, the presence of discrepancies and hernias.
If a woman suffers from severe swelling, fatigue and pain in her legs, then the doctor may recommend that she wear compression garments and will also select the right size and degree of compression. If a woman suffers from varicose veins, then she must wear compression garments, given that with this pathology the risk of thrombosis during childbirth is very high. And wearing compression garments can reduce the risk of this dangerous complication.
 Next, the doctor performs an external obstetric examination, which consists of listening to the fetal heart sounds, counting the heart rate, determining the position and presentation of the fetus, measuring the abdominal circumference and the height of the uterine fundus.
Next, the doctor performs an external obstetric examination, which consists of listening to the fetal heart sounds, counting the heart rate, determining the position and presentation of the fetus, measuring the abdominal circumference and the height of the uterine fundus.
Using an obstetric stethoscope applied to the abdomen, the doctor listens to the baby's heart sounds, determines their sonority, rhythm, the presence of noise, and counts the heart rate. This simple method allows you to identify and suspect fetal hypoxia, umbilical cord entanglement around the neck and a number of other pathologies. If, while listening to heart sounds, the doctor suspects the presence of any pathology in the fetus, then the woman is sent for additional examinations (ultrasound, CTG, Doppler, etc.), which will clarify the existing diseases or dispel all suspicions about them, revealing that the baby healthy
The position and presentation of the fetus is determined manually by palpating the head and butt through the anterior abdominal wall. It is important to know the position and presentation for the upcoming birth; these parameters are important for choosing the correct delivery tactics.
Position is understood as how the baby is positioned in the uterus - along the length of the uterus, along the width or diagonally. If the fetus rests with one end (head) on one side, and the other (butt) on the other side, and the butt and head are at the same level, then it is located in the uterus along the width, and this position is called transverse. If the fetus rests its head on one side and its butt on the other, but the butt and head are located at different levels, then it is located diagonally in the uterus, and this position is called oblique. Oblique and transverse position of the fetus are considered pathological, abnormal - from them normal childbirth through natural means is impossible. Therefore, if the baby does not turn over from an oblique or transverse position before birth, the woman will be delivered by cesarean section.
When the fetus is located in the uterus along its length, with one end (head/butt) resting on the diaphragm, and the other end is in the pelvis, then this position is called longitudinal. It is the longitudinal position that is considered normal - from it normal childbirth is possible through natural means.
For the longitudinal position, the presentation of the fetus is also determined, by which we mean which part of the fetus (head or butt) is in the small pelvis. If the head is in the small pelvis, then the presentation is cephalic, and in this case the baby will be born head first. If the butt is in the small pelvis, then the presentation is breech, and in this case the baby will have to be born legs first.
After determining the position and presentation, the doctor measures the abdominal circumference and the height of the uterine fundus (FHH) using a regular centimeter tape. The abdominal circumference at the 39th week is 94 - 99 cm. The IUD at the 39th week is on average 34 - 35 cm, but can range from 33 to 38 cm, depending on the individual characteristics of the woman.
It should be noted that at the 39th week the abdomen should already drop down slightly due to the fact that the head or butt of the fetus enters the pelvis and presses against the pelvic bones, preparing for the upcoming birth. Due to the fact that the baby descends down the abdomen, and the woman’s entire abdomen descends, and the VSDM decreases, this parameter turns out to be less than at the 36th week. However, not all women experience a drooping belly in the last month of pregnancy. Some people walk around with their bellies high and raised until they give birth. As a rule, the abdomen does not descend in women with a narrow pelvis, because the head or butt of the fetus does not have enough space between the pelvic bones that are too close together.
After examination and questioning, the doctor, if necessary, performs a gynecological examination and takes smears. These manipulations are performed only when necessary, for example, if a woman is bothered by discomfort in the genitals or if she needs to be hospitalized in a maternity hospital in advance. As a rule, a gynecological examination is performed before hospitalization to assess the condition, degree of maturity, dilatation of the cervix and its readiness for childbirth.
Based on all the examination data, tests and examinations, the doctor makes a conclusion about the woman’s condition and the need for prenatal hospitalization. So, if the pregnancy proceeded with complications, or at the 39th week any minor abnormalities were detected, then the woman is sent to prenatal hospitalization so that in the conditions of the maternity hospital, doctors prepare her body for childbirth and choose the optimal tactics and timing of delivery.
But if the pregnancy proceeded normally, then the doctor decides that the woman can carry the pregnancy to term at home and go to the maternity hospital only when contractions begin. In this case, the obstetrician-gynecologist sets the date for the next visit, which falls on the 40th week.
Warning signs
 During pregnancy, and especially in the later stages, diseases or complications may develop that lead to the death of the mother or fetus if they are not urgently treated in a hospital setting. Such severe conditions are always accompanied by symptoms, the totality of which is called alarming signs, since they indicate the development of very dangerous conditions for the life and health of both the mother and the fetus. Accordingly, every woman should know such alarming signs so that when they appear, immediately call an ambulance and be hospitalized in a hospital to receive qualified medical care, which will save her own life and save the child.
During pregnancy, and especially in the later stages, diseases or complications may develop that lead to the death of the mother or fetus if they are not urgently treated in a hospital setting. Such severe conditions are always accompanied by symptoms, the totality of which is called alarming signs, since they indicate the development of very dangerous conditions for the life and health of both the mother and the fetus. Accordingly, every woman should know such alarming signs so that when they appear, immediately call an ambulance and be hospitalized in a hospital to receive qualified medical care, which will save her own life and save the child. At the 39th week of pregnancy, the following warning signs are:
- Bloody vaginal discharge in any quantity and of any nature (color, smell, consistency, etc.);
- Copious liquid discharge from the vagina (this may look like involuntary urine);
- Frequently occurring headache, which is combined with visual impairment such as flashing spots, flashes and spots before the eyes;
- Vomiting, especially repeated;
- Sudden severe swelling of the face or hands;
- Increased body temperature above 38 o C;
- Itching and/or burning in the vagina or perineum;
- Burning and/or pain when urinating;
- Severe abdominal pain that does not decrease over time and in a state of complete rest;
- A strong blow to the stomach of any origin (for example, falling on the stomach, hitting the stomach with a hand or object);
- The appearance of more than 4 – 5 contractions within one hour;
- No fetal movements or less than 10 fetal movements in the last 12 hours.
Feelings, signs of pregnancy and changes in body condition
At the 39th week, a woman experiences a variety of sensations in various organs and systems, caused by physiological changes that have occurred in her body. These sensations, although unpleasant and uncomfortable, are physiological, that is, completely normal, and do not indicate the development of the disease. Let's consider the normal sensations of a woman at the 39th week of pregnancy, as well as their differences from pathological ones, which at first glance are very similar to normal.First of all, it is necessary to focus on the fact that at the 39th week, normal but unpleasant sensations from the digestive tract and lungs no longer bother the woman, since the uterus has dropped down and no longer presses with such force on the lungs, diaphragm, stomach. the upper intestines and other organs located above the navel. As a result, at the 39th week, heartburn, belching, digestive disorders (bloating, flatulence, etc.) and breathing problems (frequent shortness of breath, inability to take a deep breath, attacks of feeling short of air) are either absent or very rare.
In addition, a decrease in the pressure of the uterus on the small intestine and an increase in this pressure on the rectum leads to the fact that constipation goes away, but bowel movements often appear with unformed, soft, mushy or, less often, sausage-like stools. This is explained by the fact that the bolus of food now moves through the small intestine without delay, and the enlarged uterus does not put so much pressure on it. But when the contents reach the rectum, it cannot accumulate in it, since the uterus puts very much pressure on this section, which forces the intestines to empty themselves quite often and not in very large portions. Sometimes trips to the toilet are so frequent that they resemble bear sickness.
However, in addition to some relief due to the lowering of the abdomen and the entry of the head or butt of the fetus into the small pelvis, a woman at the 39th week also experiences other sensations that were not there before. These new sensations, as well as the disappearance of others that were previously present, are due to the entrance of the fetal head or butt into the small pelvis and their pressure on the pelvic bones, internal organs and soft tissues located below the navel.
Firstly, the presence of the head or butt in the small pelvis causes a strong feeling of pressure, heaviness and distension in the lower abdomen and perineum. Some women even feel the head or butt of the fetus in the pelvis between the thighs, as it presses very hard and expands the perineum. The pressure of the head or butt of the fetus on the pelvic bones and perineum provokes quite strong, clearly noticeable and unpleasant aching, pulling, stabbing and shooting pains in the lower abdomen, sacrum and lower back. These pains often radiate to the legs and cause difficulty walking.
Secondly, the pressure of the uterus on the surrounding tissues often leads to compression of the femoral nerve, as a result of which the woman suffers from persistent pain in the sacrum and on the back of the leg up to the knee.
Thirdly, even more increased pressure from the uterus on the bladder leads to frequent urination in small portions - the organ is simply not able to accumulate more urine due to the lack of free space in the pelvis. To reduce the frequency of trips to the toilet, you need to lean forward a little while urinating and urinate slowly. This promotes more complete emptying of the bladder and, accordingly, somewhat reduces visits to the restroom out of natural need.
The above sensations, which are a consequence of the lowering of the head into the pelvis, are completely normal, although unpleasant, and, in addition, they indicate the approach of labor, being their harbingers.
At the 39th week, the cervix begins to shorten, soften and partially dilate so that the tip of the obstetrician’s finger can pass through.
In addition to the described new sensations, a woman at 39 weeks also has old ones that appeared at the beginning of the third trimester and remain until childbirth. So, as before, at the 39th week there are sensations caused by an increased volume of blood and fluid in the tissues, high load on the cardiovascular system and intense metabolism (periodic sensation of heat throughout the body, increased sweating, stuffy ears, swelling, bleeding from the nose and gums). Among the above symptoms, only swelling can be either normal or pathological, while all others are absolutely normal and physiological.
If there is normal swelling, you do not need to do anything - they are not dangerous and will go away either 1 to 2 weeks before childbirth or after childbirth. And if the swelling is pathological, then it indicates the presence of a disease, and in this case it is necessary to urgently be hospitalized in the maternity hospital. Distinguishing normal from pathological swelling is relatively simple: pathological swelling increases over time, often appears suddenly in the hands and face, and can be accompanied by protein in the urine. But normal swelling can be localized on any part of the body, never suddenly appears on the hands and face and practically does not increase over time, remaining at the same level.
 Strong pressure on the bones of the pelvis, hips and legs, stretching of ligaments and tendons, as well as protrusion of the abdomen forward causes pain in the back, lower back, sacrum, coccyx, hips, pubis and pelvis and discomfort when walking, which can be both pathological and normal. Normal pain of this localization occurs in varying degrees of severity and with varying frequency in all pregnant women. And it is simple to distinguish pathological pain in the back, lower back, sacrum, coccyx, hips, pubis and pelvis from normal ones: if the pain goes away after rest, then it is normal, and if it does not decrease, then it is pathological. Accordingly, if there is normal pain in the indicated localizations, it is necessary to rest more often in a position lying on the left side and get up on all fours for 10 - 15 minutes. But if the pain is pathological, then you need to see a doctor for diagnosis and therapy.
Strong pressure on the bones of the pelvis, hips and legs, stretching of ligaments and tendons, as well as protrusion of the abdomen forward causes pain in the back, lower back, sacrum, coccyx, hips, pubis and pelvis and discomfort when walking, which can be both pathological and normal. Normal pain of this localization occurs in varying degrees of severity and with varying frequency in all pregnant women. And it is simple to distinguish pathological pain in the back, lower back, sacrum, coccyx, hips, pubis and pelvis from normal ones: if the pain goes away after rest, then it is normal, and if it does not decrease, then it is pathological. Accordingly, if there is normal pain in the indicated localizations, it is necessary to rest more often in a position lying on the left side and get up on all fours for 10 - 15 minutes. But if the pain is pathological, then you need to see a doctor for diagnosis and therapy.
Leg pain is a common sensation for women in the 39th week of pregnancy, and they can be normal or pathological. Normal leg pain is caused by swelling and heavy workload, and always improves or goes away with rest. Therefore, in order to minimize pain in the legs, you need to go to rest several times a day with your feet elevated, do not wear high heels, do not lift weights, do not sit on chairs without a backrest, do not stand or walk for a long time and do not perform other actions that increasing the load on the musculoskeletal system.
A manifestation of pathological pain in the legs is cramps of the calf muscles, when they appear, you should pull the foot towards you and hold it in this position until the pain is relieved, then massage the calf. Possible causes of cramps may be a deficiency of calcium, vitamin B 12, low blood glucose concentration and severe stress on the legs. Therefore, to prevent their occurrence, it is recommended to take calcium supplements, B vitamins and avoid heavy stress on the legs.
Often at the 39th week, women experience a periodic feeling of numbness in their arms and legs, which is caused by unknown reasons, but is not dangerous.
Also often at the 39th week, women suffer from headaches, dizziness and fainting, which can be normal and pathological. Moreover, the main difference between normal and pathological symptoms is that they decrease or disappear after resting in a dark, cool room. Normal headaches, dizziness and fainting are provoked by low blood pressure, which is typical for pregnant women at advanced stages, as well as anemia, hunger and high stress on blood vessels. And pathological headaches, fainting and dizziness (and sometimes convulsions) are caused by compression syndrome of the inferior vena cava, in which insufficient blood flows to the heart, lungs and brain, as it accumulates in the legs due to compression of the vena cava. With compression syndrome of the inferior vena cava, the symptoms do not go away after rest, and in the supine position they can only intensify. If you suspect the presence of inferior vena cava compression syndrome, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Accordingly, to relieve normal headaches, dizziness and fainting, you need to rest more often in a cool and dark room, and to prevent the development of inferior vena cava compression syndrome, you need to lie only on your side, do not lie on your back, do not sit cross-legged and avoid any poses in which the vessels of the legs can be severely compressed.
Severe stretching of the skin causes itching, stretch marks, rashes, and dry skin on the abdomen, thighs and sides. Moreover, stretch marks and dry skin are always normal, but itching and rashes can be both normal and pathological. It is easy to distinguish pathological itching and rashes from normal ones - they intensify over time and spread to other areas of the skin. And normal itching and rashes do not intensify and do not invade new areas of the skin.
Thus, if you have normal stretch marks, dry skin, itching and rashes, you don’t need to do anything, just to reduce their severity, regularly lubricate the skin of the abdomen, sides and thighs with a nourishing cream, special cosmetics or vegetable oils (for example, olive, sunflower, almond, sesame, flaxseed, grape seed oil). If pathological itching and rashes appear, you should consult a doctor.
Bleeding
Regardless of the amount of blood released, any bleeding at the 39th week should be considered dangerous. This position is justified by the fact that minor bleeding at any time can intensify and become dangerous. And heavy bleeding in the last weeks of pregnancy leads to blood loss that is incompatible with life, which can cause the death of both the fetus and the mother. Suffice it to say that heavy bleeding can lead to the loss of 500 - 1000 ml of blood in 20 minutes. Thus, it is obvious that the position of considering any bleeding in the 39th week as dangerous is completely justified.This means that if blood appears from the genital tract in the 39th week of pregnancy, you must immediately call an ambulance and be hospitalized in the maternity hospital so that doctors can carry out the necessary manipulations to save the woman and child. After calling the doctors, you should take the documents and go to bed. You cannot walk around the house and collect things, since any physical activity provokes increased bleeding. Therefore, it is necessary to wait for doctors in a lying position.
Uterus and belly
 The standing height of the uterine fundus (UFH) at the 39th week averages 34–35 cm, but can vary from 33 to 38 cm, depending on the individual characteristics of the woman. Some reduction in VSDM due to the lowering of the abdomen occurs due to the fact that the head or butt of the fetus has descended into the pelvis, preparing for childbirth.
The standing height of the uterine fundus (UFH) at the 39th week averages 34–35 cm, but can vary from 33 to 38 cm, depending on the individual characteristics of the woman. Some reduction in VSDM due to the lowering of the abdomen occurs due to the fact that the head or butt of the fetus has descended into the pelvis, preparing for childbirth. The abdominal circumference at the 39th week is 94–99 cm, and the abdomen itself protrudes very much forward. This protrusion is achieved due to the fact that the abdominal muscles relax and the uterus tilts forward.
The skin on the abdomen is greatly stretched, as a result of which it often flakes, itches, and there may be rashes and stretch marks. In the middle of the abdomen, from the navel down, there is a wide dark stripe that divides the abdomen into two halves. This line will go away after childbirth. The navel began to look like a stretched shapeless circle, or even turned outward. However, after childbirth, the navel will return to its size and shape.
When training before childbirth, the uterus periodically contracts, which is felt by the woman as false contractions. Such contractions are similar in nature to pain during menstruation, only stronger. They occur several times during the day, are quite painful, short-lived and irregular.
Pain in the abdomen and other parts of the body
 High physical stress on the musculoskeletal system and internal organs, increased weight, as well as strong pressure of the uterus on the tissues lead to the woman experiencing pain in various parts of the body. Such pain, however, is completely normal, as it is caused by physiological changes characteristic of pregnancy, and not by any disease. Let's consider these normal pains characteristic of the 39th week of pregnancy, as well as their differences from similar pathological ones (caused by diseases).
High physical stress on the musculoskeletal system and internal organs, increased weight, as well as strong pressure of the uterus on the tissues lead to the woman experiencing pain in various parts of the body. Such pain, however, is completely normal, as it is caused by physiological changes characteristic of pregnancy, and not by any disease. Let's consider these normal pains characteristic of the 39th week of pregnancy, as well as their differences from similar pathological ones (caused by diseases). Firstly, due to the lowering of the head or butt of the fetus into the small pelvis, the woman’s severity and frequency of pain in the ribs and hypochondrium decreases, but pain appears in the perineum, and abdominal pain changes its character compared to what it was at 36 th week.
Pain in the hypochondrium and ribs goes away or decreases due to the fact that the baby no longer reaches these parts of the body with his legs when he moves. Abdominal pain changes its character because the head or butt of the fetus descends into the pelvis and puts pressure on other parts of the abdomen, and also due to the fact that the uterus contracts more often and more actively, preparing for childbirth. So, at the 39th week, the pain from the pressure of the uterus and the fetal head is localized in the lower abdomen, and is of a pulling, aching, and sometimes shooting and stabbing nature. Such abdominal pain is normal and portends the imminent onset of labor.
Abdominal pain caused by the baby's movements is also normal. But in this case, the pain can be localized in any part of the abdomen, is sharp, strong, stabbing, but lasts a short period of time. In addition, abdominal pain that occurs when changing posture, trying to stand up or sit down suddenly is normal. Without a doubt, abdominal pain caused by training contractions, which have already become quite long and sensitive, is completely normal, but still remain irregular.
If you have normal abdominal pain, you do not need to do anything other than rest several times a day lying on your side or standing on all fours for 10 to 15 minutes.
Unfortunately, abdominal pain can be not only normal, but also pathological, reflecting the development of certain diseases. Normal pain, unlike pathological pain, never intensifies over time, decreases or disappears after resting in a position lying on its side or standing on all fours. But pathological pain intensifies over time, does not decrease after rest, can be localized in any part of the abdomen, has a pulling, aching, cutting or sharp cramping nature and is combined with lower back pain, elevated body temperature, vaginal discharge of blood, large amounts of turbid water or a sharp deterioration in health. If pathological pain in the abdomen appears, you must urgently call an ambulance and be admitted to the hospital, since in this case qualified medical care is needed, which will save the life and health of both the woman and the fetus.
Due to the pressure of the fetal head on the bones and tissues of the pelvis, a woman at the 39th week feels a feeling of fullness, pressure, heaviness and nagging pain in the perineum, in the pelvic bones, in the pubis, in the sacrum and lower back. Some women even feel the fetal head pressing heavily on the tissue between their thighs. Pain in the perineum and pubis often radiates to the legs, especially when walking. The pain radiating to the legs is in the nature of sharp and strong shootings, which are very unpleasant. In addition, the pressure of the head on the pelvic bones and surrounding tissues and organs leads to the fact that a woman may experience pain in the side, abdomen and back when changing position or trying to stand up suddenly. Pain, heaviness, pressure and distension in the perineum, pelvic bones, pubis, sacrum and lower back are normal. They are caused by a natural process and not by any disease. Therefore, if you have these sensations, you don’t need to do anything, just rest several times a day in a position lying on your side or standing on all fours.
High load on bones, joints and muscles, divergence of the pelvic bones to the sides, softening of ligaments and tendons, as well as protrusion of the abdomen forward provoke pain in the pelvic bones, hips, back, lower back, sacrum, coccyx, hip joints, legs, pubis and perineum, as well as discomfort when walking. These pains are normal, do not indicate pathology, and therefore do not require treatment. To minimize them, it is recommended to rest several times a day lying on your side or standing on all fours. The pain goes away when the load is reduced.
However, unfortunately, pain in the pubis, sacrum, legs and lower back is not always normal. If pain in the pubis is combined with a “duck walk” and does not decrease after rest, then this is pathological pain, which is a sign of symphysitis (inflammation of the symphysis pubis). Lower back pain is considered pathological, caused by diseases of the urinary system, if it is combined with pain during urination and/or with elevated body temperature. Pain in the sacrum of a stabbing and cutting nature, radiating to the leg and not subsiding for a minute, is also pathological. As a rule, such pain occurs due to pinching of the sciatic nerve (
At the 39th week of pregnancy, 37 full weeks have passed since the baby was conceived; according to the lunar calendar, the last tenth month of pregnancy is underway.
Changes in the fetus
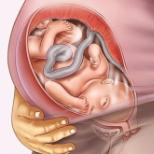
There comes a time when the fetus at 39 weeks of gestation is ready to be born at any moment. It occupies a permanent position in the uterus, and will no longer be able to change it before birth. The part of the body that is present (located closer to the exit - this is either the head or the pelvic end) has already been lowered into the small pelvis. If the baby in the stomach at 39 weeks of pregnancy is in a transverse position (this is very rare, but it does happen), natural birth is impossible, and a caesarean section cannot be avoided.
The bones of the fetal skull at this time are soft, pliable, between them there are sutures and fontanelles made of even more pliable connective tissue. Thanks to the sutures and fontanelles, as the head passes through the birth canal, it is configured and somewhat reduced in size. Immediately after birth, the head may look slightly elongated or altered in shape, but after a few days the bones return to their normal position.
The child has grown to 51–52 cm in length and weighs from 3200 to 3600 g. His weight and height depend on the conditions in which he grew up in utero and on the physique of his parents.
The appearance of the fetus at 39 weeks of gestation corresponds to a full-term newborn. The baby is in the uterine cavity in the fetal position, which will be characteristic for him for some time after birth. The movements of the fetus in the abdomen at the 39th week of pregnancy are regular and more purposeful - the baby can play with his fingers or the umbilical cord, feel his face and body, and the walls of the uterus. Monitoring the baby’s activity by his movements is very important; there should be at least 10 of them in 12 hours.
39 weeks of pregnancy is the period at which the testicles in boys should be lowered into the scrotum. If this does not happen, then we can talk about unilateral or bilateral cryptorchidism.
Changes in a woman’s body at 39 weeks of pregnancy
At 39 weeks of pregnancy, signs of labor may appear:
- Removal of the mucus plug;
- Periodic tension in the lower abdomen;
- Lowering of the abdomen.
If the belly has not dropped earlier, this can happen at 39 weeks of pregnancy. Now the height of the fundus of the uterus above the pubis is about 34 - 35 cm. The woman notes in this regard an improvement in well-being and easier breathing, since the uterus ceases to put pressure on the diaphragm with the same force.
 At the 39th week of pregnancy, the discharge from the genital tract of a fairly large amount of mucus, the consistency and appearance resembling egg white, is evidence of the passage of the mucus plug. Sometimes streaks of blood are mixed in, this is a sign that the cervix has begun to dilate. The discharge of amniotic fluid is manifested by the release of a large amount of colorless and odorless fluid from the vagina at the 39th week of pregnancy. If the fetus experienced a lack of oxygen in utero or an infection occurred, the water may be greenish in color and have an unpleasant odor.
At the 39th week of pregnancy, the discharge from the genital tract of a fairly large amount of mucus, the consistency and appearance resembling egg white, is evidence of the passage of the mucus plug. Sometimes streaks of blood are mixed in, this is a sign that the cervix has begun to dilate. The discharge of amniotic fluid is manifested by the release of a large amount of colorless and odorless fluid from the vagina at the 39th week of pregnancy. If the fetus experienced a lack of oxygen in utero or an infection occurred, the water may be greenish in color and have an unpleasant odor.
Due to the descent of the presenting part of the fetus, the pregnant woman may begin to experience constipation and frequent urination. At this stage, it is important not to miss the onset of a urinary tract infection. Normally, due to increased frequency of urination, there should be no pain at 39 weeks of pregnancy.
Despite the fact that pregnancy is coming to an end, at 39 weeks of pregnancy there is a risk of developing late gestosis. Its main features are:
- Deterioration in health;
- Headache;
- Increased blood pressure;
- Edema;
- Too much weight gain.
When labor is very close, a pregnant woman may experience an attack of diarrhea. This is how a woman’s body prepares for childbirth, so you shouldn’t be afraid of it. The onset of labor can occur in one of two scenarios - either contractions begin, or the amniotic fluid breaks first.
A pregnant woman at 39 weeks is most often already familiar with training contractions; the onset of labor is characterized by a shortening of the time between them and the regularity of their occurrence.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Each pregnancy is individual, and the expected due date is only a convention, which is calculated taking into account the date of the start of the last menstruation. If the baby has not yet been born, and the 39th week of pregnancy (41st obstetric) continues, do not worry. Such a slight overmaturity is acceptable. In what situations should labor be accelerated?
The 39th week of pregnancy from conception is not yet a long post-term period, so a woman can stay at home and is sent to the maternity hospital only with the onset of contractions or when amniotic fluid leaks. Usually, those whose pregnancy proceeded physiologically and there were no indications for an earlier delivery reach this period. The main parameters of pregnancy development at this stage are reflected in the table.
Table - Interesting facts
What happens to the fetus
The baby is completely ready to be born. Its weight on average reaches 3200-3500 g. The body weight of large children can be 4000 g or more. Height varies from 52-56 cm, and this is only an approximate figure. All systems of the baby’s body are formed and ready to exist outside the mother’s womb; nothing significant happens anymore:
- the main organs - liver, kidneys, pancreas, heart - fully cope with their tasks;
- Breathe-helping machine- surfactant has already accumulated in the lungs, which after birth promotes active independent breathing;
- gastrointestinal tract - is able to digest mother's milk, the intestines have already accumulated original tarry feces, meconium, which the baby will get rid of in the first day after birth;
- central nervous system- now and with the birth of the baby, she continues to improve;
- immunity - the mother's immune cells are actively transmitted to the fetus, because after childbirth it especially needs antibodies that can protect it from pathogenic microorganisms.
The baby's bones continue to mineralize, and the fontanelles become denser. During passage through the birth canal, the head circumference practically does not change, so a post-term pregnancy is accompanied by a greater likelihood of complicated births, and a cesarean section is more often performed.
Appearance
The baby's skin has a soft pink tint. The fluff (lanugo) and the original lubricant have completely disappeared from it, which can only remain in functional folds. Many children already have hair by the time they give birth. Almost all babies grow nails, which they can use to scratch themselves while still in the womb. The subcutaneous layer has formed, so there are no longer “wrinkles” on the child’s body. The face acquires individual features.
Movements and activity
At the 39th week of pregnancy, the fetus has already gained maximum weight and grown in size, so it is cramped for it to be in the womb. The baby continues to move, but now his activity is limited to pushing his limbs and turning his head. His arms and legs are pressed to the body, this is the position that is most favorable for the birth process. The expectant mother should continue to control movements. There should be at least ten of them per day.
Location
Normally, by the 39th week of pregnancy, the fetus lies head down along the uterus. This is the most comfortable position for passing through the birth canal. If the baby sank pelvis down, the woman is assigned to deliver by caesarean section. If the fetal weight is low and the pregnancy is repeated, natural childbirth is allowed. Cases of transverse or oblique position of the fetus are usually delivered by 39-40 obstetric weeks. If they are detected, a caesarean section is now performed.
Signs of postmaturity
You can determine whether a woman has had a pregnancy or not by looking at signs during or after childbirth. They are as follows:
- oligohydramnios;
- lack of cheese-like lubricant;
- fruit weight is about 4000 g;
- long fingernails and scalp hair;
- dense bones of the skull and reduced size of the fontanelles;
- skin greenish or yellowish.
Mother's condition
At 41 obstetric weeks, no significant changes occur with the expectant mother. If something bothered her before, the symptoms may worsen, for example, hemorrhoids worsen or back pain appears.
Now the thoughts of the expectant mother are focused on the topic of childbirth. This is an exciting period, because labor can begin at any minute.
If a woman’s belly did not drop earlier, it is happening now. Under the influence of hormones, the cervix continues to prepare for childbirth: at the 39th week of pregnancy, it shortens and softens, and the cervical canal opens.
The amount of amniotic fluid decreases; it may be yellow or even greenish, which is a sign of post-term pregnancy and intrauterine fetal hypoxia.

Discomfort
In addition to excitement and anxiety, a woman experiences many other sensations.
- False contractions. They make themselves felt more and more often; they are sometimes difficult to distinguish from physiological ones. Periodically, the stomach “hardens” at the 39th week of pregnancy - tone occurs when stroking or physical activity.
- Pressure on the perineum. A descending baby puts additional pressure on the perineal area, and the pain can radiate to the lower limbs and lower back.
- Kicking a child. Despite the fact that the pressure on the diaphragm has decreased and the stomach has dropped somewhat, the child can, with a sharp push of the leg/arm, cause the expectant mother pain in the stomach or liver, causing heartburn and even nausea.
- Pain. Possible pain in the sacrum and lower back due to pinching of the femoral nerve. The upper and lower extremities may go numb, and leg cramps may occur, especially at night.
Discharge
It is especially important to pay attention to the nature of vaginal discharge at 39 weeks of pregnancy. Normally they are:
- odorless and colorless;
- moderate and uniform consistency;
- have a mucous character.
It is acceptable to remove mucus with bloody streaks or brown color. This is the release of a mucus plug that protects the child from the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. It can be released completely or in parts. This indicates the approach of labor.
Pathological discharge (candidiasis, colpitis) should be a reason to consult a doctor. The specialist will prescribe treatment, most often these are local suppositories. Ignoring inflammation in the vagina increases the risk of ruptures during labor and infection of the fetus.
If the discharge has become liquid, abundant and has a sweetish odor, leakage of amniotic fluid cannot be ruled out. They may leak over time or come out almost all at once. If in doubt, you should immediately contact the maternity hospital. Green, yellow water or mixed with meconium is a sign of fetal distress.
Precursors of labor at 39 weeks of pregnancy
Precursors of labor are signs indicating the imminent onset of labor. A week before the onset of contractions, the following warning signs may appear:
- it is easier to breathe - due to a decrease in the height of the uterine fundus;
- nesting instinct- due to hormonal fluctuations, it is pleasant for a woman to review and put away the baby’s things, to have privacy;
- baby inactive- movements are felt less frequently, but there should be at least ten of them per day.
The mucus plug usually goes away a day or two before the onset of contractions; this may be accompanied by one-time diarrhea without signs of poisoning and without fever. Within seven to ten days (sometimes earlier), the woman begins to experience nagging pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, and sometimes uterine contractions every 10-15 minutes, but they soon pass.
Regular labor contractions can be considered contractions of the uterus every 7-10 minutes. At the same time, their frequency increases, and the rest break decreases. Precursors of labor at the 39th week of pregnancy in multiparous women may appear with the onset of active contractions.
Survey
When visiting a gynecologist, a routine examination is performed, blood pressure, intravenous mass and abdominal circumference are measured. A CTG is recorded. An ultrasound may be prescribed at the discretion of the doctor. It will help determine:
- indirect signs of postmaturity;
- baby size;
- amount of amniotic fluid;
- signs of placenta aging;
- the speed of blood flow in the uterine, fetal and placental vessels.
Need for stimulation
The normal period for the onset of labor is considered to be from 37 to 42 obstetric weeks. This is influenced by many factors: the exact date of conception, the presence of previous pregnancies, the number of fetuses being carried, the age of the woman.
If indications are identified, a decision may be made to induce labor at the 39th week of pregnancy (from conception). These include:
- mature cervix
- discharge of amniotic fluid without the onset of labor;
- oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios;
- gestosis or only swelling/increased pressure.

Methods
The following methods can be used to induce labor.
- Amniotomy. The most natural way. It involves opening the amniotic membranes using a bullet jaw. The procedure is painless. The woman feels everything as if she was undergoing a routine examination on a gynecological chair. Amniotomy can only be performed if the cervix is mature.
- Special catheter. A small-diameter balloon is installed in the cervical canal for a day. Immediately after installation, a certain amount of sterile liquid is pumped into it. In this way, mechanical pressure is applied to the cervix, and it “opens”. The catheter is removed and an amniotomy is performed.
- Drugs. For an immature cervix, hormonal drugs based on prostaglandins (Prepidil, Prostin gels) or mifepristone are prescribed. They are inserted into the vagina or taken orally.
In second and subsequent pregnancies, induction of labor has a more favorable prognosis. In primigravidas, such actions often end in an emergency caesarean section.
The 39th obstetric week is the 37th week from conception - the embryonic period of pregnancy, as well as the 39th week from the beginning of the last menstruation. 39 weeks of pregnancy means that your baby is fully mature and ready to be born. Your pregnancy is approaching the final stage - childbirth. For 75% of women, this week of pregnancy is the final one.
Dimensions of the baby at 39 weeks of pregnancy

What happens to the fetus at 39 weeks?
Your child is fully viable, all his organs are mature and ready to perform their functions outside the mother’s body. The brain is responsible for the baby’s actions and his perception of the environment. A child born at this stage is able to hear and distinguish external sounds well, and even see an object located at a distance of 20–30 cm from his eyes. It can distinguish bright colors from muted ones, and even reacts to the movement of the object in question.The mucous membrane of the mouth is rich in blood vessels and has a red color. After the birth of a child and the transition to another type of nutrition - breastfeeding - the process of absorption of food begins in his mouth. The chewing muscles and salivary glands are poorly developed. But as soon as the child begins to suck, the muscles of the masticatory apparatus very quickly become stronger. The salivary glands will begin to function only a month after birth. Special ridges are formed on the mucous membrane of the baby’s lips, which will help the newborn to grasp the breast more tightly and suck mother’s milk more actively.
At the time of birth, the liver and kidneys are able to perform their functions independently, but the process of their development in the fetus will continue for some time. The pancreas begins to produce enzymes that will break down food entering the baby's stomach.
The number of digestive enzymes has increased, and now the gastrointestinal tract is ready to accept the first food intended for it by nature - mother's breast milk. The intestines perform peristaltic movements, moving meconium (original feces) to the rectum. The digestion process will finally improve when, with the first and subsequent intakes of mother’s milk, beneficial microflora populates the baby’s intestines (now the baby’s intestines are sterile), which will contribute to the breakdown and good absorption of nutrition.
What does a baby look like at 39 weeks of pregnancy?

Childbirth is a significant challenge for a child, and despite the fact that the process is completely natural, it will require stamina and a high degree of resistance to stress. During the birth process, the child is exposed to fairly high loads from the intensely contracting uterus and narrow birth canal. Now he is gathering strength. If your baby is born with brown eyes, they will almost certainly remain that way. And if the eyes turn out to be gray or blue at birth, they may well turn into green, dark gray or brown in a few months. Like a baby's hair, the iris of the eye can still change due to the production of pigment under the influence of light. But, as a rule, the eyes only become darker.
 Now the baby looks exactly like the baby in the pictures. His skin is pink, vellus hair can remain only in folds, on his forehead and on his shoulders. The nails extend beyond the edge of the fingers and are quite sharp. The bones of the fetal skull are pliable; between them there remain pliable sutures and fontanelles formed by elastic cartilaginous tissue. This allows the head to change configuration and pass freely through the mother's birth canal. Fetal growth occurs mainly due to lengthening of the limbs and torso. The fetus has a rather large head, approximately ¼ of the body length, a well-developed chest and shoulder girdle, a rounded, protruding abdomen and a less developed girdle of the lower extremities.
Now the baby looks exactly like the baby in the pictures. His skin is pink, vellus hair can remain only in folds, on his forehead and on his shoulders. The nails extend beyond the edge of the fingers and are quite sharp. The bones of the fetal skull are pliable; between them there remain pliable sutures and fontanelles formed by elastic cartilaginous tissue. This allows the head to change configuration and pass freely through the mother's birth canal. Fetal growth occurs mainly due to lengthening of the limbs and torso. The fetus has a rather large head, approximately ¼ of the body length, a well-developed chest and shoulder girdle, a rounded, protruding abdomen and a less developed girdle of the lower extremities.
The baby's weight gain may already have stopped - this is how nature intended it to make it easier for the mother to give birth.
The fetus is more closely surrounded by the walls of the uterus than ever before, its limbs are bent and pressed tightly to the body, there is practically no room for movement, it is completely immobilized. The baby is completely ready to be born. The presenting part, be it the head or the pelvic end, descends into the pelvic cavity and does not change its position before birth.
At this stage, the baby’s active movements slow down. This is due to a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid; its renewal still occurs every 3 hours, but there is no longer enough room for movement and, as a rule, the starting position for the baby’s appearance has already been chosen. However, you should still pay attention to the amount of movement. There should still be at least 10 of them in 12 hours. The average weight of a baby at this stage is 3 kg and height 50 cm.
Fetal development at 39 weeks of gestation
- By the 39th week the baby is already fully developed. Do not be alarmed if the gynecologist says that the fetus is too large, because in fact it is very difficult to calculate the weight of the child in the womb.
- There is less and less room for movement in the mother's belly, so in later stages women notice a decrease in the child's activity.
- The child behaves quietly; he needs to gain strength before the upcoming event.
- If the scheduled date of birth has already passed, the doctor checks whether the baby has enough amniotic fluid. Even if everything is fine, you can discuss the possibility of medical intervention with your doctor. Under no circumstances try to speed up contractions on your own.
- All organs and systems are ready to function outside the womb. The baby is ready to be born.
- At 39 weeks, the lubricant that covers the skin and the fine hairs called lanugo begin to disappear. Some lubrication and lanugo may be present at birth.
- The baby receives antibodies through the placenta that protect him from diseases. He will receive additional antibodies when you breastfeed him immediately after birth; with the first drops of colostrum in the delivery room, he will receive the most important biologically active substances.
- A breech position that has persisted until this time has almost no chance of correction (3–5% of children remain in the wrong position before childbirth).
What happens in a woman’s body at 39 weeks of pregnancy
 At 39 weeks of pregnancy, a woman is looking forward to meeting her baby. The last weeks are the most difficult for her. Despite the fact that a woman waits for the first contractions to appear and the decisive moment of pregnancy arrives, the arrival of labor often comes as a surprise to her. In order not to get completely confused, prepare in advance the things that you will need in the maternity hospital, have your passport, exchange card and health insurance policy with you.
At 39 weeks of pregnancy, a woman is looking forward to meeting her baby. The last weeks are the most difficult for her. Despite the fact that a woman waits for the first contractions to appear and the decisive moment of pregnancy arrives, the arrival of labor often comes as a surprise to her. In order not to get completely confused, prepare in advance the things that you will need in the maternity hospital, have your passport, exchange card and health insurance policy with you. The abdomen drops low, the fundus of the uterus is located at a distance of 34–35 cm from the symphysis pubis. The baby's movements are felt well and the woman should control the number of movements. Ten perceptible movements in 12 hours is the norm for this period of pregnancy.
Physiological changes occur in the mother's body - the birth canal prepares for childbirth: the pelvic bones become softer, the cervix smoothes and contracts, which causes stabbing aching pain in the perineum and lower abdomen.
At 39 weeks of pregnancy, the body finishes preparing for the baby’s first feeding.
- The mammary glands reach their final size. They may increase further after childbirth until milk production begins.
- Thick yellowish milk begins to leak from the mammary glands. This is colostrum. It is rich in nutrients and antibodies that will help your baby make a successful debut.
- To prepare for your first feeding, you may want to talk to a lactation consultant or attend a breastfeeding class before your baby arrives.
Among the strongest sensations this week is an increased urge to urinate. The reason is that right now your bladder is under the most pressure in the entire 9 months of pregnancy.
While awaiting childbirth, a woman should monitor the nature of the discharge from the genital tract so that if changes occur, she can take the necessary measures in a timely manner.
Light milky discharge with a slight sour odor is considered normal at this stage of pregnancy.
Good to know
The discharge of a lump of mucus from the genital tract is most likely a sign of the release of the mucus plug, which closed the entrance to the uterus during pregnancy. The passage of the mucus plug is a sign of imminent labor.
Yellow or green discharge with an unpleasant odor should cause alarm - it is impossible to allow inflammation in the vagina now, this is dangerous for infection of the fetus and the development of postpartum complications.
Bloody discharge is also a bad sign; as a rule, it appears during placental abruption and requires immediate medical intervention.
Belly at 39 weeks pregnant
The size of your belly now seems especially huge to you. However, most likely the abdomen goes down, since the presenting part of the fetus is pressed against the entrance to the pelvis.

Vlog - 39 weeks pregnant
At this stage of pregnancy, you should already have everything prepared for the upcoming birth. The necessary things have been collected, documents have been prepared, all the necessary nuances have been agreed upon by the obstetrician who will deliver the birth: pain relief, the presence of the spouse in the delivery room, the possibility of a “caesarean section” in case of unforeseen situations.Good to know
The bag for the maternity hospital should be completely assembled, the car in the garage should be filled with gasoline, and it is best for the future father to take a vacation to help his beloved wife around the house and be close to her. This is a great time for emotional conversations, making plans for life, and it is necessary to take advantage of it to unite the family in the happy anticipation of the baby.
Try not to go far from home or out of town: if you go into labor, it may be difficult to transport you to the maternity hospital.
Think about how exactly you will go to the maternity hospital when contractions appear: whether you call an ambulance or go in your own car. If you choose your own car, discuss with your relatives which of them will take you to the maternity hospital.
Good to know
You cannot drive a car on your own during contractions.
 Don't neglect older children if you have them. Talk and explain where and why you will leave home. Tell them that you will return with your brother or sister, involve them in the general bustle, buying things, preparing the room.
Don't neglect older children if you have them. Talk and explain where and why you will leave home. Tell them that you will return with your brother or sister, involve them in the general bustle, buying things, preparing the room.
Both parents-to-be should learn how to install a child car seat before the baby gets into it. Then you won't have to waste time installing a car seat before going home from the hospital. And one more important point. Be sure to discuss with your other half its actions during childbirth.

An expectant mother should not expect to give birth in a lying position - she should continue to lead as active a lifestyle as possible, take evening walks with her husband before bed, do gymnastics, and do feasible housework. With worries and activity, the remaining days will fly by unnoticed, and mom will get rid of the painful fear of the unknown. To relax, it is useful for the expectant mother to listen to beautiful music - by the way, this will help her baby, who is also having a difficult time at this time, calm down, gain strength.
Rest should also be mandatory. Night sleep can hardly be complete now due to frequent trips to the toilet and training contractions, so be sure to rest during the day at every convenient minute - your husband can wash the dishes, the machine can wash the laundry. But no one will give you the strength to give birth if you don’t take care yourself.
Childbirth. What you need to know about the onset of labor.
How does labor begin? Usually, by 38 weeks of pregnancy, a woman has already heard many stories from her friends about contractions and the rupture of amniotic fluid. But there is usually no clear picture of when she should go to the maternity hospital.One of the harbingers of childbirth is the passage of the mucus plug, which closed the cervical canal throughout pregnancy. The mucus plug is shed as a result of the opening and shortening of the cervix and usually contains a small amount of blood.
Childbirth is also foreshadowed by the appearance of irregular contractions. The woman’s stomach feels tight, the tone of the uterus begins to increase, starting from the fundus of the uterus, then the excitement spreads to the lower segment.
Good to know
Contractions are harbingers, unlike real contractions, they are not regular, do not lead to the opening of the cervix and are not labor forces. After some time, contractions become regular, that is, at regular intervals. From this moment, childbirth actually begins.
Often, labor is heralded by the breaking of amniotic fluid. The outpouring of water contributes to the development of contractile activity of the uterus and the appearance of contractions.
At the very beginning of labor, a woman experiences a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the perineum and vagina, and pain in the lower back intensifies. In some pregnant women, the onset of labor provokes mild nausea, diarrhea, and frequent urination.
If you start having contractions, they are regular, painful and becoming more frequent - this is an undoubted sign of the beginning of the labor process. The period of contractions can last for several days or be short - up to several hours. Therefore, the first thing you should do when you feel that - yes, labor pains have begun - go to the maternity hospital.
Good to know
If the amniotic fluid has broken, then you need to go to the maternity hospital as soon as possible. Violation of the integrity of the membranes opens the way for infection from the vagina into the uterus and can lead to intrauterine infection.
Normally, natural labor should not last more than a day. Old midwives say that the sun should not rise twice over a woman in labor, and this is confirmed by modern medicine.
A full-term healthy baby greets the world with a loud cry. The criteria for full term are determined by a pediatrician - a neonatologist, but if the baby weighs more than 2.5 kg, has grown to 48 cm, cries well and actively sucks at the breast - everything is in order: you have given birth to a new healthy little person and become a mother.
Dangers at 39 weeks of pregnancy
- chronic fetal hypoxia,
- gestosis,
- premature detachment of a normally located placenta.
Any infectious processes in the body can lead to infection of the fetus, as well as postpartum complications. Avoid large crowds of people, observe personal hygiene rules.
Tests at 39 weeks of pregnancy
A consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist is necessary in order to clarify the condition of the fetus and assess the readiness of the woman’s body for childbirth. A general urine test is still required.The examinations at the reception are still the same:
- Weight measurement.
- Blood pressure measurement.
- Measuring the height of the uterine fundus and abdominal circumference.
- Listening to the fetal heartbeat using an obstetric stethoscope.
- Determining the location of the fetus in the uterus by palpating the abdomen.
- CTG (cardiotocography).
At 39 weeks of pregnancy, an ultrasound is not required. Only in certain cases can a doctor recommend undergoing an examination to determine the position of the fetus, the amount of amniotic fluid, assessing blood flow in the placenta, the length of the umbilical cord, the presence of nodes on it, and entanglement. The condition of the uterus, cervix, its degree of maturity and readiness for childbirth will also be assessed.

An ultrasound scan of the fetus at 39 weeks of pregnancy evaluates the structure of the placenta. At this stage of gestation, the placenta becomes the second or third degree of maturity, that is, it gradually ages. But despite this, antibodies continue to be actively transported through the placenta from you to the baby, forming his immune system.
Fetometry (fetal size) with fetal ultrasound at 39 weeks of pregnancy is normal
- BDP (biparietal size) 88–102 mm.
- FZ (fronto-occipital size) 109–129 mm.
- OG (fetal head circumference) 311–359 mm.
- OB (fetal abdominal circumference) 310–374 mm.
Normal dimensions of long bones on fetal ultrasound at 39 weeks of gestation
- Femur 69–79 mm.
- Humerus 61–71 mm.
- Forearm bones 53–61 mm.
- Tibia bones 60–70 mm.
Every mother eagerly awaits the birth of her baby. But sometimes it also happens that there is simply not enough patience. And often a woman wonders if she is 39 weeks pregnant. Is it possible to do this, is the child ready to be born and how can everything be speeded up - this is what I want to talk about now.
What happens at 39 weeks
At the very beginning, you need to figure out what is happening to the woman’s body at this time and whether the baby can be born. So, childbirth at 39 weeks of pregnancy is normal. The baby is already sufficiently formed to be born without fear. His position in the womb is head down, legs and arms tucked in. This means that he has already prepared for the natural process of emergence. All his internal organs are also designed to work, although for now the baby receives food through the umbilical cord, and his intestines are still sterile. It is also important to remember that at this time the child’s motor activity decreases significantly. This is due to the fact that the amount of amniotic fluid decreases, and the baby also has little free space. The child may not move for a long time, but there is nothing to worry about.
Harbingers of childbirth: distant
How can you understand that labor begins at 39 weeks of pregnancy? So, for this we can trace whether there are the first harbingers of this process. How can a lady feel at this time? So, indicators can be distant and close. If we talk about distant ones:
- The birth will be very soon when the lady's belly has sank. The woman will definitely feel it, as it will become easier for her to breathe. However, diarrhea may occur, as the baby will put pressure on the gastrointestinal tract.
- False contractions. Closer to the time of birth (however, sometimes in the second trimester of pregnancy), a woman may experience false contractions, which got their name thanks to the scientists Braxton and Hicks. In this way, the body prepares for the birth of the baby. However, the strength of these contractions is significantly lower, and the sensations are not so painful.
- Change in posture. Due to the fact that a woman's stomach drops, her center of gravity shifts. And, naturally, your posture changes. The gait becomes “duck-like.” Unpleasant sensations and discomfort in the area and sacrum may occur.

Harbingers of childbirth: close
However, there are more obvious signs that labor is about to occur. If a woman is 39 weeks pregnant, the warning signs of labor will be as follows:
- Vaginal discharge. Before birth, brown mucous discharge may appear, possibly streaked with blood. It's not scary, the mucus plug comes out. This may also indicate that something is going on
- Removal of the mucus plug. It appears in the very first weeks of the baby’s formation. Its main function is to protect the child from infections. This plug tightly closes the entrance to the uterus, which prevents viruses and infections from entering its cavity. When she leaves, this is an important indicator that labor will soon occur. However, she can go out a week before the baby is born. How can you understand that this is exactly what happened? The woman will have a thick mucous discharge, an accumulation of it, possibly streaked with blood.
- Motor activity of the baby. Before birth, the babies seem to quiet down in the stomach. The reason for this is the lack of space for active actions. The child grows up, the belly increases as much as possible, but this is not enough for the baby. Therefore, children move less.
- Changes in the cervix. A woman, of course, will not feel this, but a doctor can diagnose it. So, it is very important to track because these indicators indicate how close the woman is to active labor.
- Changes in a woman's body weight. Before giving birth, a woman’s weight most often decreases. This all happens because the pregnant woman’s body accumulates estrogen (the most important hormone for labor), which helps reduce swelling. Excess fluid is removed from the body, and the mother’s weight decreases.
- Loose stool. The accumulation of estrogen in a pregnant woman’s body also affects the condition of the woman’s stool. So, often about a week before giving birth, a woman will increasingly visit the toilet. This is the natural process of bowel movement before childbirth.
- Contractions. What else does a woman need to know if she is 39 weeks pregnant? The harbingers of labor, which indicate its initial process, are contractions. Painful sensations will gradually intensify, and the time between sensations will decrease.
And, of course, an indicator that natural childbirth is close will be psychological changes in the pregnant woman. A couple of weeks before the birth of the baby, the woman becomes calm, peaceful, and forgetful. Stops worrying about little things. This is all very important, as it helps prepare the woman for the process of labor. However, it is worth saying that all these indicators are very individual.

Intimate relationships
If a woman wants to know how to give birth faster than 39 weeks of pregnancy, she should just have sex. For a very long time, doctors tried to prohibit intimacy in the last weeks of bearing a child. And all because this is a great thing. Everything happens during a woman’s orgasm, when the body can mistake such contractions for the beginning of labor. In any case, even if this does not help intensify labor, it certainly will not harm. After all, all the positive emotions that the mother experiences are transmitted to the baby. However, it is worth remembering that at this time the woman may have little lubrication. In order not to spoil the sensations during intimacy, you need to stock up on artificial substitutes.
Nipple massage also works in a similar way. This is not only an excellent preparation for breastfeeding, but also a natural stimulation of labor.

Drinking alcoholic beverages
You can often read that natural childbirth can be significantly brought forward by drinking a little alcohol. So, ladies advise each other to take a glass of wine or even an alcoholic mixture. According to them, this forces the baby to quickly “get out” from the inside, since he does not like this kind of food at all. However, this fact is not confirmed by doctors. Moreover, doctors never tire of repeating that it is absolutely forbidden to drink alcoholic beverages at any stage of pregnancy. After all, this can affect not only the state of health, but even the development of the child himself.
Special food
Let's look further at how to give birth faster than 39 weeks of pregnancy. So, people say that you can eat certain foods, and they, in turn, speed up the process of the baby being born. What, then, is offered to the ladies:
- Spicy dishes. However, doctors have absolutely no scientific evidence for this. In addition, it is worth remembering that you should not eat raw fish (if the lady chooses Japanese cuisine).
- Olive oil. Doctors do not refuse this remedy. If you take it one tablespoon three times a day, the uterine ligaments soften and its elasticity improves. In addition, this is not only a way to speed up labor, but also a method to avoid ruptures at the time the baby is born.
- Raspberry tea. This is a common method of speeding up labor in the United States. So, you need to brew a drink from raspberry leaves and drink it starting from the 35th week. However, everything needs to be done in moderation; this must be remembered.
- Castor oil. Some women know that its use can cause contractions. However, why does this happen? The thing is that castor oil has a laxative effect. And this leads to early stimulation of the cervix.
When figuring out how to give birth faster than 39 weeks of pregnancy, it’s worth remembering that you don’t need to speed up this process yourself. Experts say that labor should be stimulated only for medical reasons. In other cases, the baby himself knows better whether it is time for him to be born or whether he needs to sit in his tummy a little longer.

Medical stimulation
Normal vaginal labor can begin any time after the 37th week of pregnancy. At this time, the baby is already fully formed and ready to see the world. However, sometimes the patient may be prescribed induction of labor (patient reviews after this are positive, because all this happens exclusively under the supervision of obstetricians). However, such a procedure should be prescribed only for special indicators.
Indicators of induction of labor before the scheduled date
In what cases can labor be stimulated for a woman in the 39th week of pregnancy?
- Multiple pregnancy. This is necessary because two or more children at this time are already very crowded in the mother’s belly.
- Medical indicators. This could be Rh conflict between mother and fetus, heart complications, or increased blood pressure. It is worth remembering that all this affects not only the mother’s condition, but also the baby himself.
- Failure during childbirth. Earlier than the appointed time, at the 39th week, a woman can be medically induced to give birth if the water breaks prematurely, the contractions are weak and short-lived, if the cervix is dilated and there are no contractions, and also if the woman is tired, exhausted and unable to can manage the process of bringing a baby into the world.

Methods of inducing labor
If a woman is 39 weeks pregnant, like So, doctors can choose one of the methods for stimulating labor.
- Apply pressure to the cervix. To do this, the woman is injected with prostaglandins, special hormones that cause the cervix to open.
- Amniotomy, i.e. opening of the amniotic sac. This procedure is painless. When the water leaves the uterus, the pressure in it increases, the baby’s head puts pressure on the pelvic bones, which stimulates the birth of the baby.
- Oxytocin. The introduction of this hormone into the body stimulates uterine contractions.

When is stimulation prohibited?
If a woman is 39 weeks pregnant (second birth, first - it doesn’t matter), induction of labor may be prohibited for her for the following reasons:
- The position of the child is incorrect, he is not ready for the normal process of birth.
- The baby’s condition is not ideal (cardiac monitor readings are important).
- The baby does not match the size of the mother's pelvis.
- The mother has certain health problems (for example, a suture on the uterus).
In all these cases, natural childbirth most often becomes impossible, and the woman is prescribed a caesarean section.