Types of hair in men on the body and what determines their amount?
Representatives of the strong half of humanity have more active hair growth along the torso than women. In fact, the presence of hair in both sexes is laid down by nature (the body area is covered with hair equally in both men and women), but in men it is clearly visible, while the female fluff is often lighter, lighter and not so noticeable. Why can hair grow so strongly in men on the body, and what functions they perform, we understand the material below.
Types of hair on the body of a man, depending on the place of growth
Trying to figure out why men grow body hair, first of all it is worth noting their structure. So, the vegetation of the representatives of the strong half of humanity is thicker, denser and tougher. That is why it is so clearly visible. In addition, the cover of vegetation on the body of a man has a pigment, in contrast to a woman's, which is weaker.
It is important to know that a lot of body hair in a man is a whole combination of certain factors, such as:
- Heredity (genetic predisposition);
- Nationality;
- Physical, hormonal and sexual health of a representative of the strong half of humanity.
Initially, trying to figure out what the hair on the body of a man is talking about and why it grows so actively, it is worth knowing that the growth activity of the body cover is formed even during the intrauterine development of the fetus. That is, the baby in the womb is covered with a thin primordial fluff - lanugo. Later, after birth, within 1-3 months, this layer of vegetation is independently erased, and already thin fluffy hair grows in its place. And only by the period of puberty they change to more mature and adult - bristly.
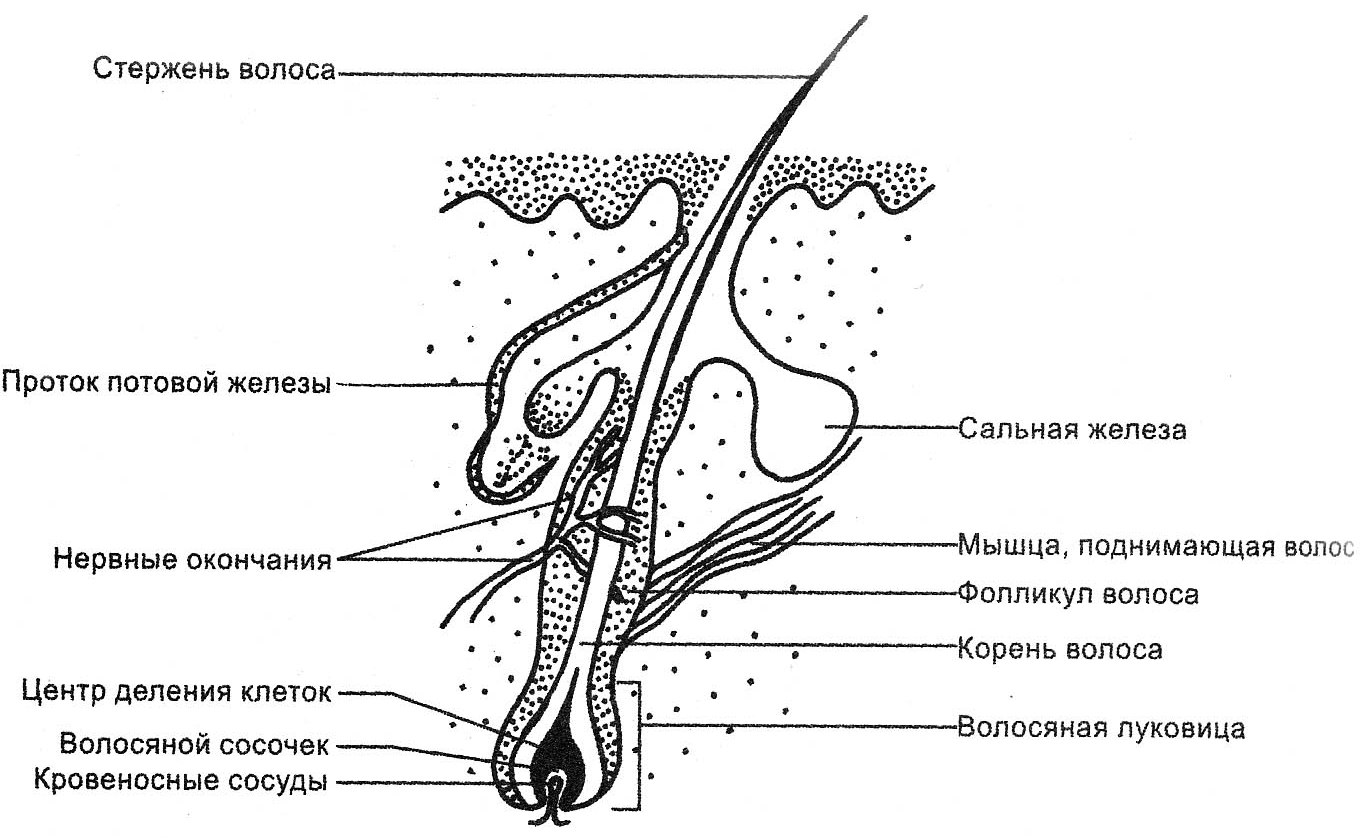
The structure of the hair consists of the following components:
- Protein - 76%;
- Water - 15%;
- Lipids - 8%;
- Pigment - 1%.
Understanding the question of why men grow body hair, it is worth classifying all vegetation into types according to their location:
- Beard and mustache. A bristly cover covering the line of the cheekbones, chin, neck and area above the upper lip;
- Pubic vegetation. Forms a cover in the groin area, somewhat affecting the lower abdomen and upper thigh;
- Hair on the chest in men. They form a cover of varying degrees of density, depending on the characteristics of the organism and nationality, as well as genetics;
- Underarm vegetation. It is an indispensable proof of the sexual maturity of a man, as well as pubic.
In addition, a certain degree of hair density is observed in men on the arms / legs, as well as on the back.
Important: the level of the male hormone testosterone is responsible for the intensity of growth of the vegetation cover on the male torso. For its production, in turn, the testes and only the anterior lobe of the actively working pituitary gland are responsible. It is noteworthy that the head is covered with hair also under the influence of testosterone, and also bald under its influence.
What is the function of body hair?

Understanding the topic “why hair grows on men on the body”, it is very important not to lose sight of the main functions that this vegetation performs. The fact is that nature has thought of everything in a person to the smallest detail. Initially, a man is a getter, a hunter, a protector. This means that he must be able to survive in difficult conditions of the wild, preserve his family and continue it. In order to help the representative of the strong half of humanity in this as much as possible, nature has genetically laid hair in his body. Thanks to this, a representative of the strong half of humanity can:
- Stay in the cold for a long time. A dense cover of vegetation along the torso allows you to normalize heat transfer and retain heat;
- It is normal to tolerate heat. In conditions of heat, the torso of a person begins to sweat. To prevent the body from cooling at a high rate through the released moisture, the hair somewhat restrains its evaporation and at the same time warms the person. That is, they perform the function of regulating heat transfer again;
- Attract a female. In a modern interpretation - like women. The fact is that the axillary and pubic vegetation is able to retain the dried male hormone-pheromone, which the chosen female (potential sexual partner) feels.
In addition to the listed functions, the hair on the torso of the "male" enhances the sense of touch and is even an erogenous zone. With a light touch to the male vegetation, it gives a signal to the nerve endings. The signal enters the brain, excitation occurs.
In addition, it is the vegetation on the torso in certain areas that prevents skin or tissue from rubbing against the skin during walking and other actions performed by a person. This is especially true for underarm and groin hair.
What determines the amount of hair in men?
Finding out the answer to the question “why men grow chest hair”, you need to know that it is testosterone that is responsible for the density and density of vegetation on the body of men. And the higher the level of this hormone, the more hairy the representative of the strong half of humanity will be. And the presence of a high level of testosterone indicates that the potential male is hardy and capable of procreation.
Also, the growth of hair on the chest is stimulated by another male sex hormone - androgens. They, along with testosterone, are responsible for the puberty of the boy. In this case, the vegetation follicle reacts very subtly to androgen, responding with growth to a natural stimulus. Normally, hair on the chest of a young man begins to appear already at the age of 16-18 years. If at 20 they are still not there, then this may signal a lack of male sex hormones androgens.
So, we found out why men have a lot of body hair and how it affects all areas of a person's life. It is worth understanding that the vegetation on the torso of a man is only a sign of masculinity. However, excessive hairiness (too thick cover over the entire body, including the back, neck) may indicate a cause such as hormonal pathology. In this case, you should contact an endocrinologist or at least a family doctor.